Name
ROS2 DDS Bridge
Description
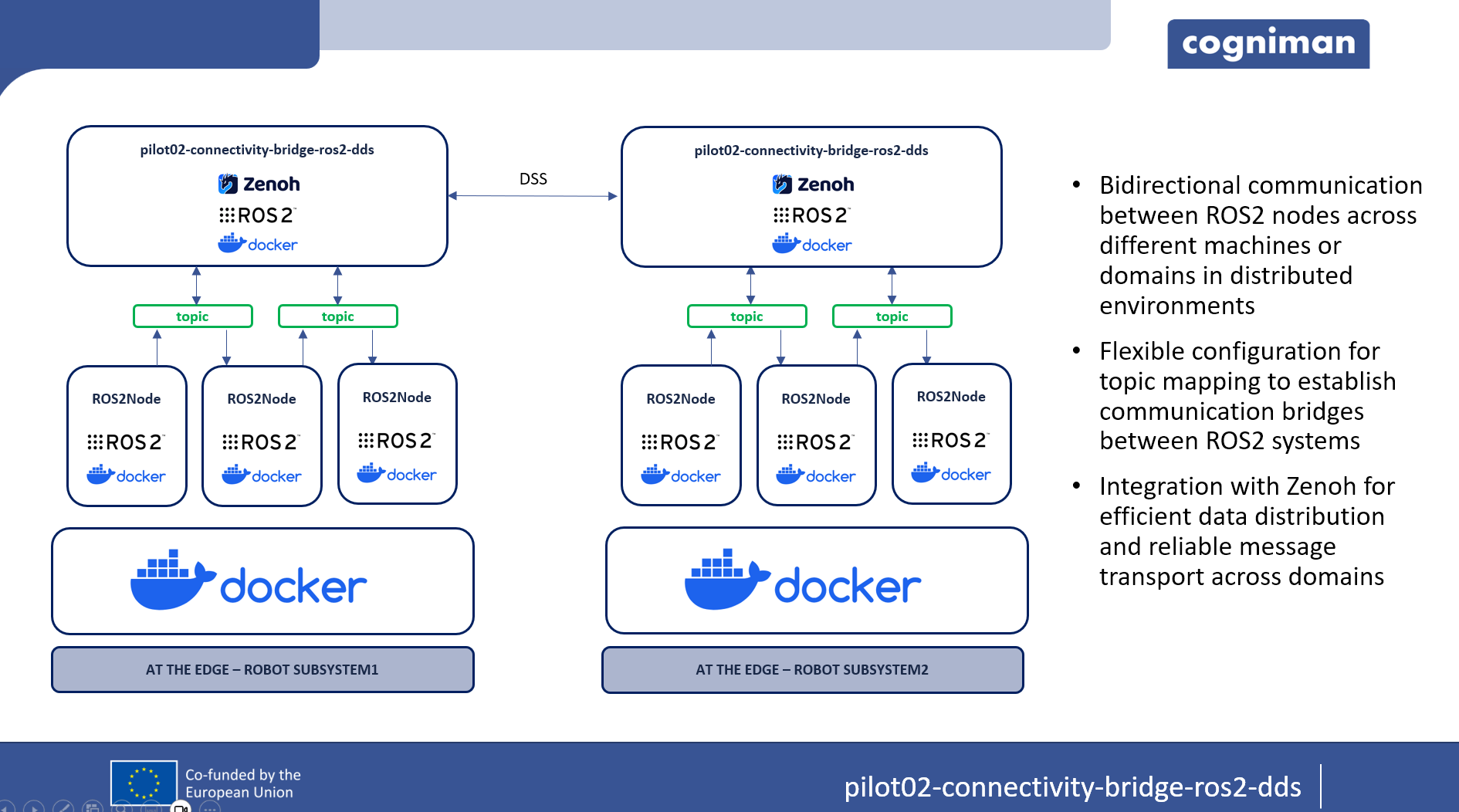
This component acts as a bridge to facilitate bidirectional communication between ROS2 nodes across different ROS2 domains in distributed environments using DDS (Data Distribution Service). Built upon the zenoh-bridge-ros2dds component from zenoh-plugin-ros2dds, this software enables seamless interoperability between ROS2 systems on separate domains, allowing for flexible message exchange and configuration of communication topics.
Features:
- Bidirectional communication between ROS2 nodes across different ROS2 domains.
- Topic configuration to establish communication bridges between specified topics.
- Docker Compose-based test automation that validates interoperability between a publisher and a subscriber in different ROS2 domains through a bridge client and a bridge peer.
- Built on zenoh-bridge-ros2dds, leveraging Zenoh for robust data distribution between distributed systems.
The repository includes the following components:
- Configuration files to set up topic mappings and manage ROS2 domain IDs.
- Docker Compose environment for automated testing and validation, simulating a publisher and subscriber in different ROS2 domains connected through a bridge client and peer.
- Zenoh integration for efficient message transport between ROS2 systems.
Type
Tool
Layer
Connectivity
HRL
2.8
Partners

Pilot
This component will be used to enable interaction between ROS2 subsystems running in a distributed manner across different machines or domains. It provides the necessary communication bridge, ensuring seamless interoperability between ROS2 nodes in separate domains or networks. By facilitating bidirectional communication over DDS (Data Distribution Service), this component allows ROS2 systems to exchange data effectively, even when they are geographically separated or operating in different environments. This is particularly useful in scenarios where distributed ROS2 subsystems must work together, enabling collaborative and coordinated operations across diverse network setups.
In particular, it will be used in the GOIMEK pilot to achieve interoperability between subsystems such as the AGV, robotic arm, sensor, control system, and HMI (Human-Machine Interface).



